Solenoid valves are electromechanical valves used to control the flow of fluids or gases. Adamant Valves manufactures solenoid valves for organizations seeking to provide the following services: release, mix, shut off, meter, or dispense fluids or gases.
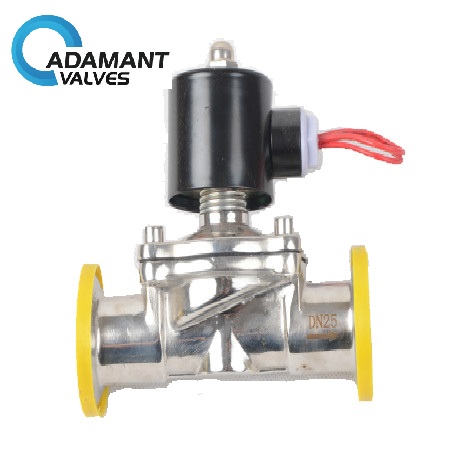

They are very popular in a variety of industries because of the advantages they offer in terms of safe and fast switching, reliability, long service life, and compact design. However, they are most commonly used in the residential, electrical, industrial, and commercial industries.
Some common applications include refrigeration, HVAC and air conditioning, power washing, agricultural air conditioning, pneumatic and hydraulic systems, compressed air systems, automotive engineering, and household appliances.
History of Solenoid Valves
The first solenoid valve was the solenoid control valve, marketed and manufactured by ASCO Numatics in 1910. Then, in the 1950s, manufacturers began selling plastic molded solenoid valves. The switch to plastic meant that solenoid valves were now more efficient, more reliable, and resistant to corrosion and chemicals.
This trend of improvement continued into the late 20th century. For example, beginning in the 1970s, manufacturers began producing automatic shut-off solenoid valves, which were safer and easier to operate than manually controlled shut-off valves.
In the 1990s, governments around the world, as well as independent organizations, began standardizing solenoid valves, which led to more frequent international trade, easier cooperation between companies, and easier maintenance. Today, newer standards also limit the use of hazardous substances in valve manufacturing to improve their environmental friendliness. Today, many valve manufacturing and use innovations are focused on health and sustainability.

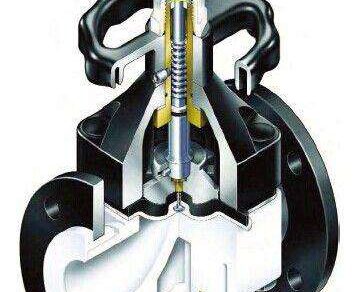
Design of Solenoid Valves
Production Processes
Manufacturers produce solenoid valves through a variety of processes, such as CNC machining, laser welding, injection molding, coil winding, and deep-draw machining of solenoid valve housings. Once they have manufactured the valve components, they assemble them.
These components include solenoid valve iron housing, magnetic retainer, magnetic isolation sleeve, solenoid valve coil, valve, air inlet, air outlet, spring, throttle hole, and actuator. The solenoid also has seals.
Materials of Solenoid Valves
Adamant Valves has a wide variety of materials that they can use to make their solenoid valves. Valves can be made from plastic and metal materials such as PVC, natural polypropylene, PTFE, CPVC, stainless steel, bronze, aluminum, and brass. Seals, such as Viton seals or Buna N seals, are usually made of some type of rubber. Sometimes, manufacturers make stainless steel seals.
Design and Customization of Solenoid Valves
Solenoid valve manufacturers make selections based on application specifications such as natural fluid/gas in the pipeline (corrosive, hazardous, viscosity, acidity, etc.), environment, frequency of pipeline use, and application standard requirements. Based on specifications, they can choose design aspects such as valve size, valve material, valve type and configuration, and the number of ports.
Suppliers can customize your solenoid valve system in a number of ways. For example, they typically create valves with two connection areas and one orifice, but they can also make your valve with three connection areas and two orifices. Similarly, while they typically design valves to run on 12-volt DC power, they can customize them to run on 3-, 6-, or 24-volt power. They can also provide you with specialized: pressure levels, spring return, valve sizes, etc.
Features of Solenoid Valves
Solenoid valves use two main components to function: the solenoid coil and the valve. The coil is a magnetized wire coil that becomes active through a series of charges and then sends a current. This current creates a magnetic field that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy to move the actuator. The actuator is an extension of the valve; it is responsible, along with the attached string, for moving the valve from the open position to the closed position.
Solenoid valves are typically constructed as normally closed (NC) or normally open (NO) devices. Normally closed valves operate using an internal plunger rod or pin called a plunger, held in place by a solenoid coil that blocks the flow of current. To activate flow in an NC valve, an electromagnetic charge must be sent through the coil, which then lifts the plunger off to allow flow. On the other hand, the opposite is true for NO valves. When the solenoids are activated, they close.
Types of Solenoid Valves
Solenoid valves are defined by three general components to help manufacturers select the best valve.
1. the material is controlled, such as solenoid water valves and solenoid air valves
2. valve construction/design, such as proportional solenoid valves, three-way solenoid valves, and plastic solenoid valves
3. How they are powered, such as 12-volt solenoid valves and pneumatic solenoid valves
Solenoid water valves
Solenoid water valves, also known as hydraulic solenoid valves, direct the flow of water through a pilot-operated, normally open valve.
Solenoid gas valve
Solenoid gas valves, also known as gas solenoid valves, air valves, or pneumatic solenoid valves, regulate the flow of air and gas by means of a diaphragm and gas pressure. They are capable of maintaining regular pressures, such as those used for home heating and cooling, and extremely high pressures, such as those used for power tool operation.
Proportional solenoid valves
Proportional solenoid valves work in the same way as regular pneumatic valves, except that they have more advanced flow control capabilities, which allow them to establish variable flow rates proportional to the valve’s electrical control signal.
12 Volt Solenoid Valves
The 12-volt solenoid valves come with 12 volts and are powered by their DC power supply.
Solenoid valves are either pilot-operated or direct-acting.
Pilot Operated Solenoid Valves
A pilot-operated solenoid valve is a combination of a hydraulic or pneumatic valve and a smaller solenoid valve that uses a diaphragm rather than a plunger to create a differential pressure to control flow.
Direct-acting solenoid valves
Direct-acting solenoid valves use a plunger that is in direct contact with the opening into the valve body, called the orifice. In this case, the plunger opens and closes the orifice to control flow.
Semi-direct-acting solenoid valves
Semi-direct-acting solenoid valves draw on the attributes of both direct-acting and indirect-acting valves. This allows them to operate from 0 bar (0 psi) when dealing with high flow rates. Typically, they are used in high-pressure applications.
High-Pressure Solenoid Valves
High-pressure solenoid valves are an excellent resource for flow control in areas where they are not compatible with other valves.
Stainless Steel Solenoid Valves
Stainless steel solenoid valves, as the name implies, have a stainless steel body. Because stainless steel is corrosion and wear-resistant, stainless steel solenoid valves are suitable for chemical processing applications that require excellent control of alkalis, acids, and analytical reagents.
Miniature Solenoid Valves
Miniature solenoid valves are the perfect size for precision medical equipment such as biotechnology equipment, portable medical devices, and gas analyzers.
Butterfly Valves
A butterfly valve is a solenoid valve that regulates or isolates the flow of fluid. Its closing mechanism is a rotating disc located in the center of the pipe, and a rod carries it through the pipe to an actuator on its exterior. As the actuator rotates, the disc also rotates, perpendicular or parallel to the flow. The butterfly valve is always present in the flow.
Actuated Ball Valves
The actuated ball valve is so named because it contains a ball with a small hole in the center, which helps it control the flow of material through the pipe and an actuator that rotates the ball. When the actuator rolls the ball, the flow begins or stops. One of the most common types of ball valves is the three-way ball valve, which has three ports. First, the actuated ball valve is used to start and stop the flow, but not necessarily to control it. Actuated ball valves are best suited for high flow applications and applications that require a manual operation option.
Tubular Solenoid Valves
A tubular solenoid valve is simply a tubular solenoid valve. They are typically used for DC power applications only.
Poppet Valves
Poppet valves sometimes referred to as mushroom valves, consist of an oval or circular bore and a disc-shaped tapered plug located at the end of a shaft called a stem. The poppet valve can be closed or opened to control engine air/gas flow and timing. It is made of stainless steel or brass.
Brass Solenoid Valves
Brass solenoid valves made of brass are ideal for use with non-corrosive substances such as inert gases, water, or light oils. They are not strong enough to carry highly corrosive substances.
PTFE Solenoid Valves
PTFE solenoid valves made of PTFE, also recognized by its brand name Teflon, are an excellent choice for harsh gases and corrosive fluids.
Benefits of Solenoid Valves
There are many reasons to purchase solenoid valves. With fewer moving parts than other valves, solenoid valves are relatively low-maintenance. They can also be operated by remote devices, a valuable feature for hazardous applications. In addition, they can be made portable. Finally, solenoid valves are flexible; capable of using hydraulic or pneumatic power.
Solenoid Valves Accessories
Typical solenoid valve accessories include connectors, manifolds, screws, washers, and lights. Of these, connectors are the most common. They can help you assemble more complex valve assemblies.
Properly Maintaining Solenoid Valves
With a little care, your solenoid valve will last a long time. One way to care for your valves is to clean them regularly according to a set schedule. With the proper tools, you can do this without completely disassembling the valve assembly. In addition to regular cleaning, if you notice leaks, excessive noise, or slow operation, you should clean your valves as soon as possible.
To improve valve system performance, avoid using mismatched fluids, as doing so can cause early wear. Also, never allow the contents of the valve to freeze. Likewise, always keep the valve contents at the proper temperature and pressure.
Solenoid Valves Standards
The standards your solenoid valve needs to comply with depending on your application, industry, and location.
For example, if your valve will come in contact with potable water, your solenoid valve must be lead-free. In the United States, drinking water and plumbing codes require RO (reverse osmosis) equipment to be NSF certified and/or comply with NSF 61-G (leachate and lead-free regulations developed by NSF (National Science Foundation)). If you are going to use your solenoid valves abroad, they need to be certified as lead-free by NSF International and approved by ANSI and the Canadian Standards Board.


Recent Comments